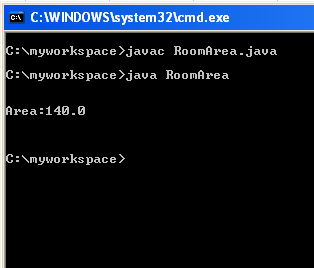
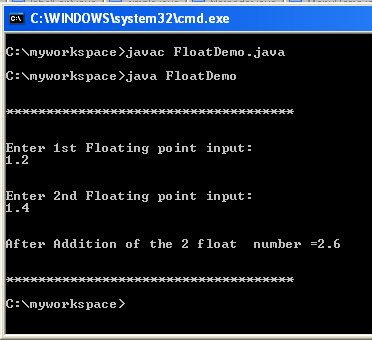
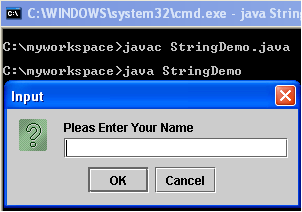
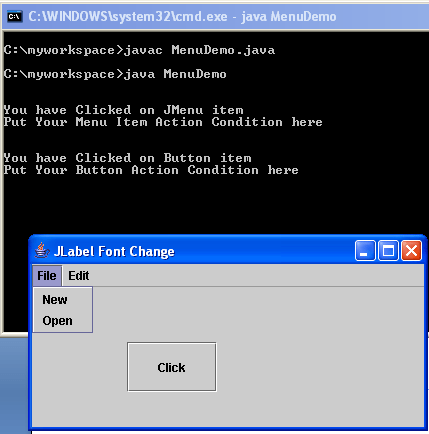
In my previous example I have shown about How to add TextField (JTextField)in java.
Here I will try to show how to add validation in JTextField.
Suppose,I am trying to prepare a Calculator and I don’t want my user to give invalid input at the first keypress entry, for example, Plus (+) or Minus (-).
But, they can give any numeric entry at the first keyPress.So, I need to put validation in my JTextField so that Plus (+) or Minus (–) sign will not be allowed at the first keypress /key entry, but they are allowed after any numeric or digit entry.
In the given example, if users press (+) or (–) sign at first, our program will show error message but it will allow users to take numeric entry at first. After first entry, (+) or minus (-) will be allowed.


Code Example:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Calc extends JFrame
{
JTextField ques, answer;
private Toolkit toolkit;
char ch;
int plusOccurs=0;
public Calc()
{
JPanel panel =new JPanel();
getContentPane().add(panel);
panel.setLayout(null);
setSize(300,200);
setTitle(“Easy Calculator”);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
toolkit=getToolkit();
Dimension size=toolkit.getScreenSize();
setLocation(size.width/2-getWidth()/2, size.height/2-getHeight()/2);
ques=new JTextField();
answer=new JTextField();
JButton calculate=new JButton(“Calculate”);
calculate.setBounds(75,50,90,30);
ques.setBounds(10,10,220,30); // Positioning of TextField(JTextField)
answer.setBounds(10,100,220,30); //Positioning of TextField(JTextField)
panel.add(calculate);
panel.add(ques ); // Adding TextField(JTextField) in JPanel
panel.add(answer ); // Adding TextField(JTextField) in JPanel
ques.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter()
{
public void keyTyped(KeyEvent e)
{
ch=e.getKeyChar();
if (ch==’+’ && ques.getText().length()==0)
{
System.out.println(“\n”);
System.out.println(“Sorry, You have entered :”+ch+”:at first,Please Enter Numeric value, then try”);
ques.setEditable(false);
ques.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
}
else if (ch==’-‘&& ques.getText().length()==0)
{
System.out.println(“\n”);
System.out.println(“Sorry, You have entered :”+ch+”:at first,Please Enter Numeric value at first”);
ques.setEditable(false);
ques.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
}
else
{
ques.setEditable(true);
ques.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
}
}
});
}