In my last post I have shared about How to show Bangla(Bengali) in JLabel.
Here I am going to share you about the detection of click event on Java swing .components.
In out java programming we usually use addActionListener to detect any type of action performed on java components. For example we can add addActionListener on JMenuItem, JButton etc.
Here I have given how to add actionListener in an easiest way and also about how to detect which component is being clicked.
There are various ways by which you can do the same work. But I found the below procedure is the easiest one.
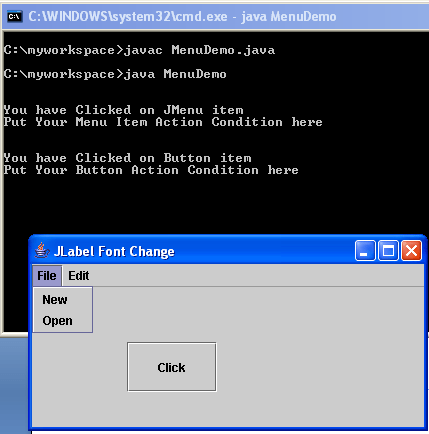
OUTPUT:
Code Example:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class MenuDemo extends JFrame implements ActionListener
{
JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar();
JMenu menu = new JMenu(“File”);
JMenu menu1 = new JMenu(“Edit”);
JMenuItem item1 = new JMenuItem(“New”);
JMenuItem item2 = new JMenuItem(“Open”);
JButton myButton=new JButton(“Click”);
public MenuDemo()
{
setJMenuBar(menuBar);
setVisible(true);
setSize(400,200);
menuBar.add(menu);
menuBar.add(menu1);
item1.addActionListener(this);
myButton.addActionListener(this);
menu.add(item1);menu.add(item2);
JPanel panel=new JPanel();
setTitle(“JLabel Font Change”);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
getContentPane().add(panel);
panel.setLayout(null);
myButton.setBounds(95,55,90,50);
panel.add(myButton);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
if(e.getSource()==item1){
System.out.println(“\n”);
System.out.println(“You have Clicked on JMenu item”);
System.out.println(“Put Your Menu Item Action Condition here”);
}
else if(e.getSource()==myButton){
System.out.println(“\n”);
System.out.println(“You have Clicked on Button item”);
System.out.println(“Put Your Button Action Condition here”);
}
}
catch(Exception exc){
Exception newEx = new Exception(“Error at:”+new java.util.Date()+””,exc);
newEx.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[]args)
{
MenuDemo ex=new MenuDemo();
ex.setVisible(true);
}
}